Arbeitsblatt: Staatsformen & Gewaltenteilung / Systems of Government & Division of Power
Material-Details
EIn Arbeitsblatt (auf Englisch) über Staatsformen (Einheitsstaat, Bundesstaat, Staatenbund) und Gewaltenteilung. Ideal für englischsprachigen W&G Unterricht. Lösungen für den ersten Teil sind im Arbeitsblatt enthalten.
Geschichte
Politik
klassenübergreifend
4 Seiten
Statistik
111542
1307
5
14.02.2013
Autor/in
Daniela Rohrbach
Land: Schweiz
Registriert vor 2006
Textauszüge aus dem Inhalt:
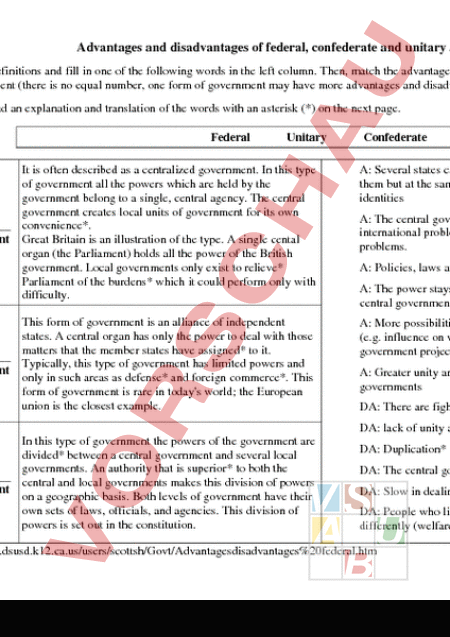
Advantages and disadvantages of federal, confederate and unitary systems of Government Read the definitions and fill in one of the following words in the left column. Then, match the advantages (A) and disadvantages (DA) with each of the forms of government (there is no equal number, one form of government may have more advantages and disadvantages than another). You can find an explanation and translation of the words with an asterisk (*) on the next page. Federal Unitary Confederate It is often described as centralized government. In this type of government all the powers which are held by the government belong to single, central agency. The central government creates local units of government for its own convenience*. Government Great Britain is an illustration of the type. single cental organ (the Parliament) holds all the power of the British government. Local governments only exist to relieve* Parliament of the burdens* which it could perform only with difficulty. A: Several states can cooperate in issues that are of interest to all of them but at the same time they can keep also to keep their own separate identities This form of government is an alliance of independent states. central organ has only the power to deal with those matters that the member states have assigned* to it. Typically, this type of government has limited powers and Government only in such areas as defense* and foreign commerce*. This form of government is rare in today world; the European union is the closest example. A: More possibilities to become part of the decision-making process (e.g. influence on what is taught in schools and where highways and government projects are going to be built). A: The central government can spend more time on national and international problems because the local government deals with local problems. A: Policies, laws and administration are uniform* in the whole country A: The power stays at local levels, which prevents* the growth of large central government A: Greater unity and stability, fewer conflicts between national and local governments DA: There are fights over power (national supremacy* vs state rights) DA: lack of unity and common laws In this type of government the powers of the government are divided* between central government and several local governments. An authority that is superior* to both the central and local governments makes this division of powers Government on geographic basis. Both levels of government have their own sets of laws, officials, and agencies. This division of powers is set out in the constitution. DA: Duplication* of services DA: The central government is out of touch* with local concerns DA: Slow in dealing with local problems DA: People who live in different parts of the country will be treated differently (welfare*, legal systems etc.) Flash-card vocabulary Confederate government Staatenbund Federal government Bundesstaat Unitary government Zentral-/Einheitsstaat *Exercise-specific vocabulary assign select and give responsibility, appoint beauftragen, zuteilen foreign commerce Aussenhandel to be out of touch with sth to have lost contact with sth, to have no contact with sth den Kontakt verloren haben, keinen Kontakt haben to prevent keep sth from happening, hinder vorbeugen, verhindern burden an unpleasant duty or task Last to relieve remove responsibility, release erleichtern, entlasten convenience benefit, comfort, enjoyment Belieben, Behagen superior higher, better, exceeding übergeordnet defence protection system, security, resistance Abwehr, Verteidigung supremacy domination Vorherrschaft, Obergewalt, Souveränität to divide to separate trennen, aufspalten uniform identical, equivalent einheitlich duplication to copy, to make sth double Verdoppelung, Vervielfältigung welfare aid, assistance Sozialhilfe, Fürsorge Unitary government A: Uniform policies, laws, political, enforcement, administration throughout the country A: Greater unity and stability, fewer conflicts between national and local governments DA: Central government out of touch with local concerns DA: Slow in meeting local problems Confederate Government A: Keeps power at local levels, which prevents the growth of large central government A: Makes it possible for the several states to cooperate in matters of common interest and also to keep their own separate identities DA: lack of unity and common laws Federal Government A. Local government/officials have to be responsive to people who elect them A: Central government can devote more time and energy to national and international problems because the local government handles local problems A: More opportunities for participation in making decisions (for example in influencing what is taught in the schools and in deciding where highways and government projects are going to be built) DA: Duplication of services DA: People who live in different parts of the country will be treated differently (welfare, legal systems etc.) DA: There are disputes over power (national supremacy vs state rights) Da die SuS nicht für jede Person in der Klasse Karten schreiben können, würden die SuS den Auftrag erhalten, wöchentlich die erstellten Karten am Computer abzutippen und in einer Excel-Tabelle auf Google Docs hochzuladen, in welchem eine Vorlage für die Karten verfügbar ist. The Division of Power 1) What does the term division of power mean? Define it. 2) What are the three powers called? Underline them. legislative power economic power judicial power national power medial power ruling power ecological power executive power 3) Is the division of power important in democratic system? What would happen if division of power did not exist? 4) At what levels does the division of power exist? State canton municipality (Gemeinde) at all three levels